The New SEO Frontier: Optimizing WordPress for LLMs and AI Search
I. Introduction: The Shift from Search Engines to Answer Engines
For nearly two decades, the goal of SEO was painfully clear: rank higher, earn clicks, win traffic.
Everything revolved around blue links.
We optimized for impressions, fought for position zero, obsessed over CTRs, and measured success by how many humans clicked through to our WordPress sites.
That era is quietly ending.
Today, search is no longer just about links. It’s about answers.
Instead of scrolling through ten results, users now ask ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Perplexity, or emerging AI assistants a question—and get a single synthesized response. No SERP. No clicks. Often, no visit at all.
And here’s the uncomfortable truth most WordPress site owners haven’t processed yet:
If your site isn’t cited, referenced, or retrieved by AI systems, your brand effectively doesn’t exist in the future of search.
Traditional SEO optimized content for keywords.
Large Language Models (LLMs) optimize for context, structure, entities, and data clarity.
This gap is where a new discipline is forming.
What Is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of structuring content, data, and technical architecture so that AI systems can accurately parse, retrieve, trust, and cite your site when generating answers.
Think of GEO as the next evolution of technical SEO—not a replacement, but a new standard layered on top.
Because in an AI-first web:
- If machines can’t parse your content, humans never see it.
- If AI can’t retrieve your data, it can’t cite your expertise.
- And if your WordPress site isn’t AI-readable, your authority evaporates.
II. How LLMs “Search” Your WordPress Site
To optimize for AI, you first need to understand how AI systems actually interact with your site—because it’s fundamentally different from Googlebot.
Crawlers vs. Training Data: Clearing the Confusion
Traditional SEO revolves around crawlers like Googlebot, which index pages continuously and rank them later.
LLMs operate in two distinct modes:
- Training Crawlers
Bots like GPTBot collect large-scale data to train foundational models. This data is static, historical, and not tied to live queries. - Retrieval Crawlers (RAG Systems)
Modern AI search tools use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Instead of relying solely on training data, they fetch live content from the web at query time.
This distinction matters.
Blocking GPTBot might prevent training usage—but blocking retrieval access can completely remove your site from AI-generated answers.
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
RAG is the backbone of AI search.
Here’s the simplified flow:
- A user asks a question (e.g., “How does GEO differ from traditional SEO?”)
- The AI searches live sources for relevant content
- It retrieves structured, authoritative pages
- It synthesizes an answer using retrieved data
- It cites sources—or silently incorporates them
Your WordPress site isn’t being “ranked” in this system.
It’s being evaluated for usefulness, clarity, and factual reliability.
The Context Window Problem
LLMs operate within a finite context window.
That means:
- Bloated HTML
- Excessive DOM nodes
- Long-winded intros
- Repetitive fluff
…all reduce the chance your content survives retrieval and synthesis.
Clean structure isn’t just UX anymore—it’s token efficiency.
III. Technical Pillar 1: Advanced Schema & JSON-LD (The AI “Map”)
If content is the message, schema is the map that tells AI where everything lives.
And most WordPress sites are still using kindergarten-level schema.
Why Basic SEO Schema Is No Longer Enough
Plugins like Yoast and Rank Math do a decent job—for Google.
But LLMs don’t infer meaning the same way humans or search engines do. They prefer explicit, machine-readable facts.
This is where JSON-LD structured data becomes foundational for GEO.
Deep Schema Implementation for LLMs
Instead of generic Article schema, advanced WordPress sites should implement:
- TechnicalArticle for tutorials and guides
- FAQPage for concise, extractable answers
- Product schema with rich attributes
- HowTo schema for procedural content
- Person and Organization entities
Each schema layer reduces ambiguity.
AI doesn’t guess.
It extracts.
Knowledge Graph Integration: Entity-Based SEO
LLMs think in entities, not keywords.
Your WordPress site should clearly define:
- Who you are
- What you specialize in
- How concepts relate to each other
This means linking:
- Authors → expertise → articles
- Products → features → use cases
- Concepts → definitions → references
When done correctly, your site becomes a mini knowledge graph, increasing AI trust and citation likelihood.
IV. Technical Pillar 2: Managing AI Crawlers (The New robots.txt)
For years, robots.txt was simple.
Allow Google.
Block spam.
Done.
Not anymore.
The Opt-In vs. Opt-Out Debate
Some publishers rushed to block AI crawlers out of fear—copyright, training misuse, content theft.
But here’s the risk:
If you block AI retrieval, you block visibility in AI answers.
No citation.
No reference.
No brand presence.
That’s not protection—that’s invisibility.
Key AI Crawlers to Know
Your WordPress robots.txt may now reference:
- GPTBot
- OAI-SearchBot
- ChatGPT-User
- CCBot (Common Crawl)
Each serves a different purpose.
Smart Permissions Strategy
The emerging best practice:
- Allow retrieval and search
- Limit or restrict training where appropriate
- Protect premium content behind authentication
- Monitor crawler behavior via server logs
This isn’t about blocking AI.
It’s about controlling how AI interacts with your site.
V. Content Architecture for AI Readiness
LLMs don’t read like humans.
They scan, segment, extract, and prioritize.
Your WordPress content architecture must reflect that reality.
The Inverted Pyramid 2.0
Old SEO advice said: hook readers, tease answers, build suspense.
AI hates suspense.
For GEO:
- Start with direct, factual answers
- Expand with explanation
- Support with examples
- Then add nuance
This structure increases snippet eligibility and retrieval accuracy.
Semantic Formatting as Navigation
H2s and H3s are no longer cosmetic.
They function as semantic anchors for LLMs.
Each heading should:
- Represent a single concept
- Avoid vague language
- Match query intent
- Contain extractable meaning
Well-structured headings guide AI through your logic like a table of contents.
Why “Fluff” Is Now a Ranking Liability
AI systems favor signal over style.
Pages with excessive storytelling, filler paragraphs, or keyword padding often get ignored during retrieval.
In GEO, clarity beats cleverness.
VI. Performance & Accessibility: Why Speed Is an AI Metric
Page speed has always mattered—but now it matters to machines, not just humans.
Tokenization Efficiency Explained
LLMs process content as tokens.
Bloated WordPress themes waste tokens on:
- Nested divs
- Inline styles
- Unused scripts
- Visual clutter irrelevant to meaning
Every wasted token reduces extraction accuracy.
HTML Minification & DOM Reduction
Technical GEO optimization includes:
- Clean semantic HTML
- Reduced DOM depth
- Minimal inline JavaScript
- Efficient markup hierarchy
The result? Faster AI parsing and higher retrieval success.
API-First Content Delivery
Advanced setups use the WordPress REST API to serve clean, layout-free content to AI agents.
This creates a separation between:
- Human-facing design
- Machine-facing clarity
And that separation is powerful.
VII. Measuring Success: The Challenge of AI Attribution
Here’s the frustrating part.
You won’t always see AI traffic.
The Dark Traffic Problem
Visits from AI systems often appear as:
- Direct traffic
- Unattributed referrals
- Zero-click visibility
Your content may influence thousands of decisions without a single measurable click.
Tracking AI Citations
New tools and methods are emerging to:
- Detect brand mentions in AI outputs
- Monitor citations in Perplexity
- Track inclusion in ChatGPT answers
This is still early—but visibility beats precision.
The New KPI: Inclusion Rate
Forget rankings alone.
The future metric is:
How often is your brand included in AI-generated answers for your topic?
That’s GEO success.
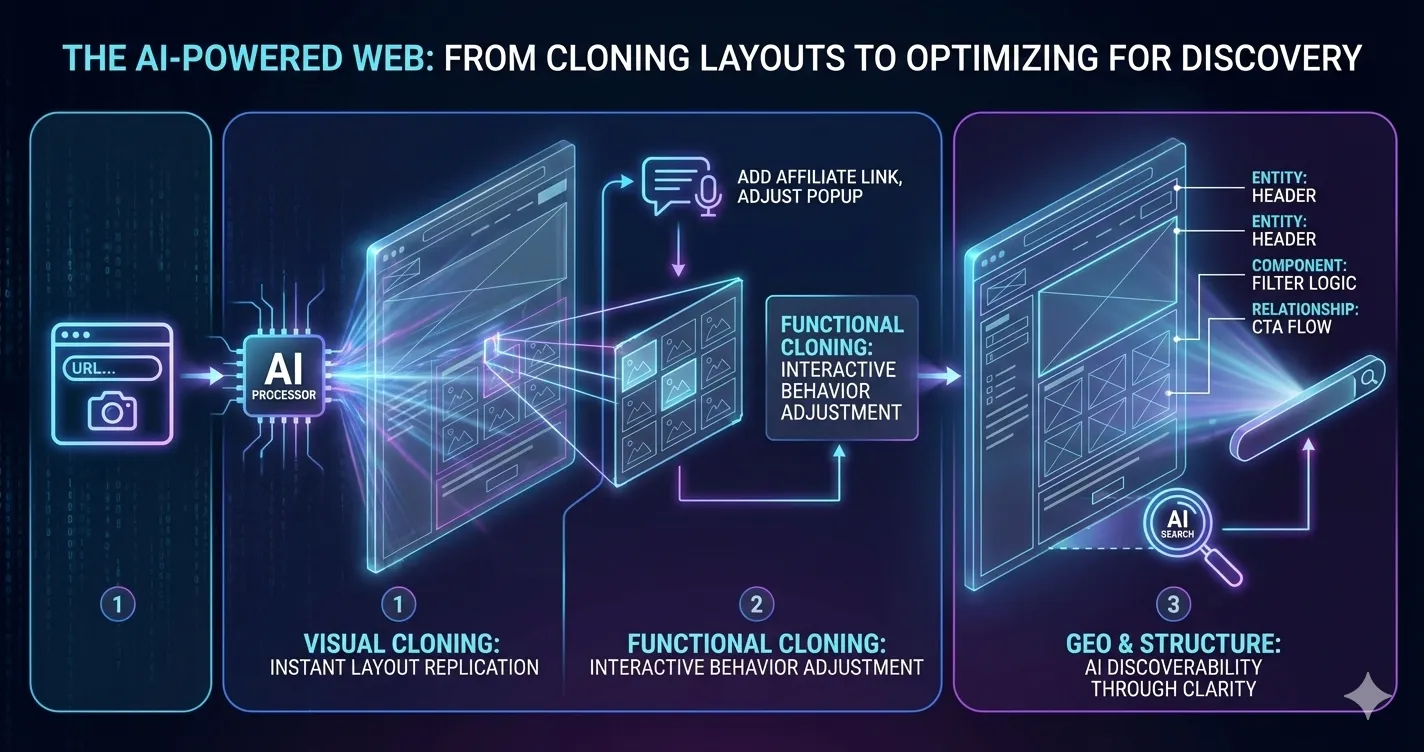
AI isn’t just changing how websites are found—it’s changing how they’re built. Tools showcased in recent viral demos can now clone an entire website’s layout, structure, and visual hierarchy in minutes, simply by pasting a URL or uploading a screenshot. What used to take hours inside page builders like Elementor can now be replicated almost instantly, giving developers and marketers a fast way to prototype, analyze layouts, and rebuild designs without touching the original code.
But the real shift isn’t visual cloning—it’s functional cloning. Modern AI tools can now replicate interactive behaviors, not just static designs. Popups, filters, dynamic galleries, call-to-action flows, and even monetization elements like affiliate links can be recreated and modified through natural language instructions. Instead of rebuilding features manually, creators can instruct AI to adjust specific sections, reposition elements, or add new functionality—turning AI into something closer to a semantic page builder than a simple generator.
This acceleration matters for GEO because it reveals how AI understands the web: not as pages, but as systems of components and functions. The same way AI can identify a popup module or filter logic, it also identifies entities, sections, and relationships when retrieving content for search answers. Websites that are cleanly structured, modular, and semantically clear don’t just clone better—they’re also easier for AI search engines to parse, retrieve, and trust. In an AI-first web, clarity isn’t just good design—it’s discoverability.
VIII. Conclusion: Future-Proofing Your WordPress Site
Generative Engine Optimization isn’t replacing SEO.
It’s what SEO is becoming.
Search engines ranked pages.
AI systems retrieve knowledge.
And WordPress—the most powerful publishing platform in history—must now evolve from a blogging tool into a structured data engine.
The web is turning into a database for AI.
So the final question isn’t whether GEO matters.
It’s this:
Is your WordPress site organized like a messy desk… or a clean spreadsheet?
Your Next Step
If you want your site to survive—and lead—in the age of AI search:
- Audit your schema
- Clean your structure
- Optimize for entities
- Respect token efficiency
- Think like a machine, not just a marketer
Download our GEO Checklist or subscribe for the next deep dive into AI-ready WordPress plugins and architectures.
Because the future of visibility won’t belong to the loudest voice.
It will belong to the most understandable one.
Core Technical Keywords Used Naturally:
- Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- JSON-LD Structured Data
- GPTBot / OAI-SearchBot
- Semantic HTML
- Entity-Based SEO
- Tokenization efficiency
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in simple terms?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the process of optimizing your website so that AI tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and Perplexity can correctly understand, retrieve, and cite your content when generating answers. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on rankings and clicks, GEO focuses on inclusion, accuracy, and machine readability.
2. How is GEO different from traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO optimizes for search engines and keywords, while GEO optimizes for AI systems and structured understanding. GEO emphasizes semantic HTML, JSON-LD structured data, entity relationships, and clean architecture so AI models can efficiently process and trust your content during Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
3. Does optimizing for AI search replace Google SEO?
No. GEO does not replace SEO—it extends it. A well-optimized WordPress site should support both Google’s crawler-based indexing and AI’s retrieval-based systems. In practice, strong GEO foundations often improve traditional SEO performance as well.
4. How do AI tools like ChatGPT access live WordPress content?
AI search tools use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). When a user asks a question, the AI retrieves relevant live content from the web, processes it within a context window, and synthesizes an answer. If your WordPress site is well-structured and accessible, it can be included or cited in that response.
5. Should I block GPTBot or other AI crawlers in robots.txt?
Blocking AI crawlers can prevent your content from being used for model training, but it may also remove your site from AI-generated answers. Most experts recommend allowing AI retrieval bots while protecting premium or private content, rather than fully blocking AI access.
6. Why is JSON-LD structured data critical for GEO?
JSON-LD structured data gives AI explicit, fact-based signals about your content. It removes ambiguity and helps LLMs identify authors, topics, products, FAQs, and relationships between entities. This significantly increases the likelihood of accurate retrieval and citation.
7. What type of schema works best for AI optimization?
For GEO, advanced schemas such as TechnicalArticle, FAQPage, HowTo, Product (with rich attributes), Person, and Organization perform better than generic Article schema. These formats align closely with how LLMs extract structured knowledge.
8. How does content structure affect AI visibility?
AI systems rely heavily on semantic structure. Clear H2 and H3 headings, concise sections, direct answers, and minimal fluff help LLMs navigate your content efficiently. Poor structure or excessive filler can cause AI systems to ignore your page entirely.
9. Why does WordPress site speed matter for AI search?
AI systems process content using tokens. Heavy themes, bloated HTML, and large DOM trees reduce tokenization efficiency, making it harder for AI to parse your page. Faster, cleaner WordPress sites are more likely to be retrieved and used in AI answers.
10. How can I measure success if AI traffic doesn’t show in analytics?
AI-driven visibility often appears as dark traffic or no traffic at all. Instead of focusing only on clicks, GEO success is measured by inclusion rate—how often your brand or content appears in AI-generated answers across platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity.

